Discovery of the cell
All the living things are made up of one or more cells. for this reason, cells known as the building block of life. cells were discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. he looked at a thin slice of a cork under the microscope that he had made, and saw that it was made up of many small box-like structures. the boxes were separated from each other by a partition.he called these boxes, cells. what Hooke actually observed were dead cells in the cork.however, even 150 years after Robert Hooke Discovery, not much was known about the cell until improved microscopes with high magnifications were made. today scientists use high magnification microscopes to study cells. they use stains(dyes) to color parts of the cell to study their detailed structure.
the cell theory
In 1838, two German biologists Mathias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann put forward the cell theory of life. the main points of this theory are as follows:
- all living things are made up of the cell, just as a wall is made up of a bricks. hence, cell are the basic building block of the living organisms. they are Complex living structures.
- all cells are similar in the basic structure and function but are not identical. they differ in size and structure.
- new cell are formed due to the division in old cells.
- the organization of a cells in the body of a living organism determines its structure.
- the way and organism functions depends on the way the cell work.
Unicellular and Multi-cellular organisms
you are aware that organisms, which is Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena and bacteria made up of one cell each. these are examples of unicellular organisms. although made up of a single cell, they perform all the activities necessary for life. they grow,move,digest,food give out wastes and reproduce. all these activities are carried out by a single cell.plants and animals that you can see around you with the naked eye are made up of many cells. they are Multi-cellular organisms. it is estimated that a fully grown human has about 100 trillion cell or Multi-cellular organisms begin life as a single cell, which is fertilized egg. the fertilized egg cell multiplies and the number of a cells increases as the organism develops.
you know that in a multi-cellular organism, the lower levels of organization are as follows:
in the organization of the living world, cells represent the lowest level called cellular level. life activities in a multi-cellular organism are performed by a group of specialized cells forming different tissues, which in turn form organs.
structure
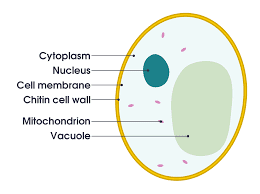
cytoplasm
the cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that makes up most of the inside of a cell. all life functions take place in the cytoplasm.
cell membrane and cell wall
surrounding the cytoplasm is a thin covering called the cell membrane or plasma membrane. the cell membrane separates the cell from its surrounding.
it protects the cell and gives it a shape. however, it allows water, minerals and some other necessary substances to pass though it. in addition, plant cells have cell wall which is absent in animal cells.
the cell wall supports and protects the plant cell since plants do not have a skeletons for support. present in the cytoplasm are smaller structures called organelles.
nucleus
floating within the cytoplasm in the center is a small spherical body called the nucleus. the nucleus is the control center of the cell. it directs the growth of the cell and controls all the activities that go on within the cell. it can, therefore, be compared to the brain in animals.
 the liquid in the nucleus is called Nucleoplasm. it is separated from the cytoplasm by a thin nuclear membrane.
the nuclear membrane is porous and allows the movement of a materials an
element of the material between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. present
inside the nucleus is a smaller spherical body
called the nucleolus. also present in the nucleus are thread like structures called chromosomes. these carry genes which
contain all the information needed by the cell to function and to
reproduce further cells of the next generation. thus,genes responsible
for the inheritance transfer of characteristic from the parent
to the offspring.
the liquid in the nucleus is called Nucleoplasm. it is separated from the cytoplasm by a thin nuclear membrane.
the nuclear membrane is porous and allows the movement of a materials an
element of the material between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. present
inside the nucleus is a smaller spherical body
called the nucleolus. also present in the nucleus are thread like structures called chromosomes. these carry genes which
contain all the information needed by the cell to function and to
reproduce further cells of the next generation. thus,genes responsible
for the inheritance transfer of characteristic from the parent
to the offspring.the nucleus and the cytoplasm together make up the Protoplasm which is called the living substance of the cell. the main constituent element of protoplasm are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen but it contains other elements also.
organelles
scattered in the cytoplasm are small structures called organelles. there are various type of organelles that perform different function. some of these are as follows:
- mitochondria are small Rod-like structures. they are oxidize to provide energy. they are ,therefore, often called the powerhouse of the cell.
- vacuoles are a sac-like structures. they store food, water and wastes. plant cells have large vacuoles as compared to animals cells .
- plant cells have organelles called the plastids present in the cytoplasm. they are of different colors and types. green colored plastids are called the chloroplasts. they contain the green color pigment chlorophyll which provides green color to the leaves. you have that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis. animal cells do not have chloroplasts.
- In addition, there are the Golgi bodies that secrete substance such as enzymes.





0 Comments